A 60-Second Overview
Regardless of your industry, the report is a valuable read for accountants, and we recommend reading it in full. Here is a quick summary of its major points:
- IT is important because "every aspect of government depends on IT."
- Globally, only 29 percent of IT projects are rated "successful."
- Success is defined as:
- On Time
- On Budget
- Achieving Expected Value
- Success depends on:
- People
- Planning
- Consultation
- Governance
The report is an absorbing read, but it fails to elaborate on a significant element: What is "value," and how do you calculate it?
What about "Value"?
The report uses the word "value" 57 times without defining it explicitly. The only comment on how to achieve it is to assess:
- Alignment of the project with the organization’s specific needs, priorities, and strategies
- Contribution to the organization’s desired outcomes
- Cost
- Level of risk
ROI to Assess Value Before & After
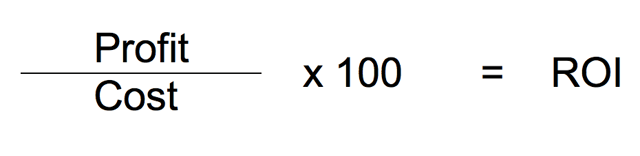
- Public sector organizations typically do not think in terms of profit.
- Even if you work outside the public sector, you may reasonably ask, "How does an ERP system (for example) generate profit for any organization?"
"Profit" (and therefore "ROI") may seem like a non-starter. But with a minor change in terminology—replacing "profit" with "calculable benefit"—the concept is applicable to the public sector. The "calculable" part is important; you don't want this exercise to dissolve into imprecise speculation about intangible benefits. Those may also warrant a discussion, but you should not give up the important quantitative analysis. You should focus on those aspects to which you can assign a real dollar value.
There are two broad categories of calculable benefits that you should consider:
Efficiency of Staff Resources
Your staff spends their entire working lives involved with IT systems. A more efficient, convenient, and highly automated solution will help them do their work faster, more reliably, and with less cross-checking and manual review required. If you estimate the hours that a new IT system might save, and multiply it by your staff's hourly cost, you can measure the economic impact of those time savings.
Reduction or Avoidance of Direct Expenses
There are many direct expenses that a new IT system can help reduce or eliminate. You pay fees to an external accountant—would those fees be reduced if you automated a significant portion of the work they performed? What if your new system could help avoid late payment of invoices and thereby reduce your late fees and penalties to vendors? Perhaps a new system would provide a reduction of ongoing annual maintenance and support costs.
An Example
Consider a scenario in which your current ERP system is no longer supported. You determine that the risk level of continuing with an unsupported system is unacceptable. You have identified three possible solutions and are working through the selection process. You have seen demonstrations and received fee estimates. You have contacted references and determined each option's strengths and weaknesses.
Clearly, there are many considerations (some of which are intangible). But don't underestimate the value of performing an ROI calculation.
- Calculable Benefit: How much money will we save with each solution? For example, estimate the following separately for each solution:
- Hours of staff time saved by reduced data processing
- Hours of staff time saved by automating report creation
- Estimate avoided late payment fees to vendors due to improved A/P processing abilities
- Decreased finance costs due to accelerated AR collections
- Cost: What is the cost of each solution including all features/modules etc. necessary to facilitate the above benefits over a 5 or 10 year period?
3 Advantages of This Approach
1) Forces Detailed Assessment: All too often we see clients who have only a general understanding of how a particular system will help them. Vendors often do little to help, aside from offering marketing double-talk: "Work Smart", "Improve Productivity", or "Improve Efficiency." These aspirational comments are great, but you need measurable results.
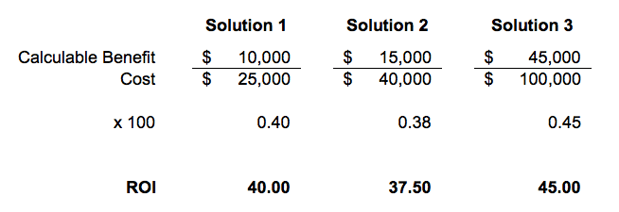
2) Easy Comparison of Alternatives: You can immediately begin to see some interesting relationships between the options that were hard to see at first:
- Solution 3 is four times as expensive as Solution 1, but it provides 4.5 times the value. If all else is equal, and the organization can find the $100,000 budget, Solution 3 is the better choice for your organization.
- Solution 2, while more expensive than Solution 1, does not provide a commensurate increase in benefit. Thus, if the budget did not allow for $100,000 investment, the next best option is Solution 1.
3) Clear Monitoring of Performance: Another advantage of this approach is that your team has identified very specific, measurable goals to monitor the project and assess success. For example, you estimated a calculable benefit value based on specific time savings in report creation and data entry. These time savings should be measured to determine whether you achieved the benefit. Moreover, if your vendor is confident in their abilities to deliver these time savings, you can attempt to include attainment of the advantages in the contract.
"IT-enabled projects aren’t just about technology—they involve substantial changes to an organization’s culture, business processes, and customers. These projects are really IT-enabled business change. A successful project improves services and allows for more effective use of taxpayer money. And their success or failure is about more than just being on time and on budget, it’s also about achieving expected value."
–Carol Bellringer, FCPA, FCA Auditor General, British Columbia
In sum, ROI calculation is an important tool that allows finance teams to estimate, measure, and demonstrate the value of their IT project.
© 2025 FH Black Inc. All rights reserved. Content may not be reproduced, excerpted, distributed, or transmitted without prior written consent.




